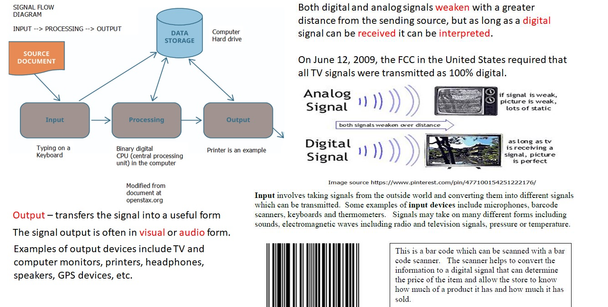
Description
The Analog Versus Digital Signaling Learning Package for Middle School Science introduces students to a survey of the basic differences between analog and digital signaling. The contents of the package includes a reading and writing activity well suited for distance learning, completion notes with an associated PowerPoint, as well two worksheets with answers. The 19 pages of student activities will facilitate student engagement and understanding. All materials are highly editable to meet your needs. With the exception of the PowerPoints, all activities are in both word and pdf format. Answer keys are included for all items.
Specifically these activities will:
- provide structured reading and writing activities to reinforce learning
- present relevant diagrams and illustrations
- provides structured notes to facilitate the delivery of content
- aligns to the Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) and Common Core Standards
- provides opportunities to demonstrate understanding of key concepts
Specific Package Contents
- Signaling Reading and Writing Activity (8 pp.)
- Analog and Digital Signaling Worksheet (4 pp.) (25 questions)
- Analog Versus Digital Signaling Completion Notes (5 pp.)
- PowerPoint to accompany the completion
- Analogue and Digital Signals Video Worksheet (1 p.) (5 questions)
- NGSS, Common Core Standards and Learning Goals (1 p.)
NGSS Standard
MS-PS4-3. Integrate qualitative scientific and technical information to support the claim that digitized signals are a more reliable way to encode and transmit information than analog signals.
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
RST.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts.
RST.6-8.2 Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; provide an accurate summary of the text distinct from prior knowledge or opinions.
RST.6-8.9 Compare and contrast the information gained from experiments, simulations, video, or multimedia sources with that gained from reading a text on the same topic.
WHST.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Learning Goals
Upon the completion of this topic the student will be able to:
1. define the term signal in reference to the transfer of energy.
2. list two basic properties of all signals.
3. explain what is meant by an analog signal.
4. recognize that an analog signal is continuously variable.
5. list devices using an analog signal.
6. list some factors that result in the distortion of analog signals.
7. recognize that distortion of an analog signal means the signal input and output will not be the same.
8. explain what is meant by a digital signal.
9. recognize that computers use a binary digital signal in their functioning.
10. recognize that unlike analog signals, digital signals do not have infinite variations.
11. recognize that electrical, magnetic and weather phenomena are less likely to interfere with a digital signal than an analog signal.
12. explain why digital signals are a more reliable way to send information than an analog signal.
Terms of Use
Purchase of the product is for classroom use by the purchaser only. It is a violation for individuals, schools, and districts to redistribute or sell this item to other individuals.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Check out Monday's Rescue for more great resources!