Description
The content contained in this learning bundle provides materials to teach a complete electricity unit for a high school physics class. This bundle contains 26 pages of scaffolded completion notes with a supporting PowerPoint, many worksheets and quizzes, an electricity exam and two lab activities which use Phet computer simulations (Coulomb's law and Circuits). With the exception of the PowerPoint
all documents are available in word (which easily edits to meet your needs) and pdf formats. Answer keys are included for all items. The bundle contains the PowerPoint and 115 pages of learning materials. Answer keys are not included in the page count. The specific contents of the bundle are listed below:
- Electricity Scaffolded Completion Notes (26 pp.)
- PowerPoint to accompany the Scaffolded Completion Notes (74 slides)
- Electrostatic Forces Worksheet (32 questions) (6 pp.)
- Electrostatic Forces quiz (31 questions) (7 pp.)
- Electric Fields and Voltage Worksheet (37 questions) (7 pp.)
- Electric Fields and Voltage quiz (33 questions) (7 pp.)
- Current, Charge and Resistivity Worksheet (50 questions) (6 pp.)
- Current, Charge and Resistivity Quiz (25 questions) (5 pp.)
- Series Circuit Worksheet (19 questions) (4 pp.)
- Parallel Circuit Worksheet (21 questions) (5 pp.)
- Series and Parallel Circuit quiz (25 questions) (5 pp.)
- Electrical Energy and Power Worksheet (27 questions) (4 pp.)
- Electrical Energy and Power quiz (25 questions) (4 pp.)
- Coulomb's Law Simulation Lab Activity (5 pp.)
- Circuit Simulation Lab Activity (14 pp.)
- Circuit Simulation Lab quiz (20 questions) (3 pp.)
- Electricity Exam (40 questions) (9 pp.)
- Learning Objectives (including NGSS and Common Core) (4 pp.)
Topics including in this learning bundle include; subatomic particle properties, law of charges, methods of charging, conservation of charge, elementary charges, Coulomb's law, calculating electrostatic force, electric fields, electric field strength, potential difference, Ohm's law, factors influencing resistance, calculating resistivity, static and current electricity, requirements for a circuit, series and parallel circuits (including representing circuits and their calculations), Kirchoff's first and second laws, electrical power and many others.
The contents of this bundle are well suited for use in a traditional classroom. They may also be easily utilized to support remote learning situations.
NGSS Standards
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
HS-PS2-4. Use mathematical representations of Newton’s Law of Gravitation and Coulomb’s Law to describe and predict the gravitational and electrostatic forces between objects.
HS-PS3-1. Create a computational model to calculate the change in the energy of one component in a system when the change in energy of the other component(s) and energy flows in and out of the system are known.
HS-PS3-2. Develop and use models to illustrate that energy at the macroscopic scale can be accounted for as a combination of energy associated with the motions of particles (objects) and energy associated with the relative position of particles (objects).
HS-PS3-5. Develop and use a model of two objects interacting through electric or magnetic fields to illustrate the forces between objects and the changes in energy of the objects due to the interaction.
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
WHST.9-12.7 Conduct short as well as more sustained research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question) or solve a problem; narrow or broaden the inquiry when appropriate; synthesize multiple sources on the subject, demonstrating understanding of the subject under investigation.
WHST.11-12.8 Gather relevant information from multiple authoritative print and digital sources, using advanced searches effectively; assess the strengths and limitations of each source in terms of the specific task, purpose, and audience; integrate information into the text selectively to maintain the flow of ideas, avoiding plagiarism and overreliance on any one source and following a standard format for citation.
WHST.9-12.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
SL.11-12.5 Make strategic use of digital media (e.g., textual, graphical, audio, visual, and interactive elements) in presentations to enhance understanding of findings, reasoning, and evidence and to add interest.
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively.
MP.4 Model with mathematics.
HSN-Q.A.1 Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays.
HSA-SSE.A.1 Interpret expressions that represent a quantity in terms of its context.
HSA-SSE.B.3 Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression.
HSN-Q.A.2 Define appropriate quantities for the purpose of descriptive modeling.
HSN-Q.A.3 Choose a level of accuracy appropriate to limitations on measurement when reporting quantities.
Learning Objectives
Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to:
1. define the term electrostatics.
2. list the three major kinds of subatomic particles and indicate their charge, mass and location in the atom.
3. define the term atomic mass unit.
4. explain why electrons are more easily gained or lost by atoms than other subatomic particles.
5. define the terms ion, anion and cation.
6. state the law of charges.
7. explain how the friction method can be used to charge some objects.
8. explain how conduction can produce a charge on a previously uncharged object.
9. explain how induction can produce a force of attraction between a charged object and a neutral object.
10. explain how the electroscope may be used to detect the presence of an electric charge.
11. state the law of the conservation of charge.
12. recognize electric charge is a scalar quantity.
13. explain what is meant by an elementary charge.
14. recognize the coulomb is the SI unit of charge.
15. calculate the mass to charge ratio of an electron.
16. recognize the net charge on an object is always a whole number multiple of an elementary charge.
17. state Coulomb's law and relate electrostatic force to changes in charge quantity and the distances between charges using this law.
18. calculate the electrostatic force between two charges of known quantity and separation distance using Coulomb's law.
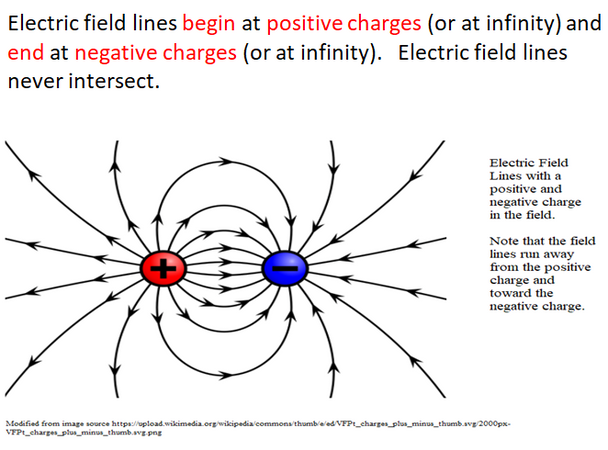
19. explain what is meant by an electric field, electric field line and a test charge.
20. recognize the direction of an electric field is in the direction of the force on a stationary positive test charge in the field.
21. recognize the force in an electric field is tangent to curved field lines.
22. draw the electric field lines associated with positive and negative test charges.
23. describe the distribution of the electric charges on the surface of a sphere.
24. recognize the electric field strength within a closed hollow conducting sphere is zero.
25. define the term electric field strength.
26. use the formula E=Fe/q to calculate electric field strength, electric static force or charge in coulombs.
27. recognize the electric field and electric force between two oppositely charged plates that are close together is uniform.
28. recognize an electric charge will tend to accelerate toward a plate having an opposite charge from itself.
29. realize work is required to move a charge toward a plate having an opposite charge from itself.
30. define the term potential difference.
31. recognize potential difference is a scalar quantity.
32. use the formula V=W/q, to calculate potential difference, work or charge.
33. define the terms volt and electron volt.
34. state the major difference between static and current electricity.
35. explain what an electric circuit is.
36. define the term electric current.
37. define the function of an electric switch and represent it in a drawing of an electric circuit.
38. recognize an ampere is an SI unit of electric current.
39. define the term coulomb.
40. use the formula I=∆q/t in calculations
41. recognize an ammeter is used to measure current in an electric circuit and represent an ammeter in a drawing of an electric circuit.
42. list three conditions required for a functioning electric circuit.
43. state the function of an electric cell or battery and properly represent these in an electric circuit.
44. recognize a voltmeter is used to measure the potential difference in a circuit and represent a voltmeter in a drawing of an electric circuit.
45. indicate the direction of current flow in a circuit.
46. define the term conductivity.
47. recognize that electrons can move easily in conductors.
48. explain why insulators limit electron flow.
49. list examples of conductors and insulators.
50. define the term electrical resistance.
51. describe Ohm's law and use the equation R=V/I in calculations.
52. define the term ohm.
53. list and discuss three factors influencing the resistance of a conductor.
54. define the term resistivity.
55. recognize the SI unit of resistivity in the ohm●meter.
56. utilize the formula for resistivity, R=ΡL/A in calculations.
57. state the roles of resistors and variable resistors and label these in circuit diagrams.
58. state some major differences between series and parallel circuits.
59. calculate current, potential difference and equivalent resistance in a series circuit.
60. state one major advantage of parallel circuits over series circuits.
61. calculate current, potential difference and equivalent resistance in parallel circuits.
62. explain what is meant by a combination circuit.
63. briefly explain Kirchhoff's first and second laws.
64. define the term power.
65. recognize the watt is the metric unit of power.
66. recognize electric power is the product of potential difference and current.
67. derive several formulas for electric power.
68. perform calculations involving electric power.
69. recognize the total electric energy in a current is equal to the power consumed and the time the current flows.
70. perform calculations involving electric power.
Terms of Use
Purchase of the product is for classroom use by the purchaser only. I do encourage you to use and edit these documents to suit your needs with your own students in distance learning environments.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.