Description
The Photosynthesis, Respiration and Energy Transfer Learning Activities Package for Middle School Science introduces students to basic concepts involving photosynthesis, respiration and energy transfer. Topics discussed include photosynthesis, factors influencing photosynthesis, aerobic cellular respiration, lactic acid and alcohol fermentation, muscle fatigue, the interactions between photosynthesis and respiration, feeding terminology, food chains, food webs and energy pyramids. The contents of the package include a reading and writing activity, lab activities, completion notes with an associated PowerPoint, as well as two worksheets and a unit exam. The 72 pages of student activities will facilitate student engagement and understanding. All materials are highly editable to meet your needs. With the exception of the PowerPoints, all activities are in both word and pdf format. Answer keys are included for all items. Specific information about the materials in this package are in the list that follows:
- NGSS, Common Core and Local Learning Objectives (2 pp.)
- Photosynthesis, Respiration and Energy Interactions Completion Notes (18 pages)
- PowerPoint to accompany the Completion Notes (54 slides)
- Feeding Relationships Reading and Writing Activity (17 pp.) (64 questions)
- Respiration and Photosynthesis Worksheet (10 pp.) (50 questions)
- Energy Transfer Worksheet (10 pp.) (28 questions)
- Photosynthesis Online Simulation Lab (8 pp.)
- Yeast Respiration Lab ( 4 pp.)
- Muscle Fatigue Lab (4 pp.)
- Photosynthesis, Respiration and Energy Transfer Unit Exam (11 pp.) (50 questions)
NGSS Learning Standards
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
MS-LS1-6. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of matter and flow of energy into and out of organisms.
MS-LS1-7. Develop a model to describe how food is rearranged through chemical reactions forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism.
MS-LS2-3. Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem.
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
RST.6-8.1 Cite specific textual evidence to support analysis of science and technical texts.
RST.6-8.2 Determine the central ideas or conclusions of a text; provide an accurate summary of the text distinct from prior knowledge or opinions.
WHST.6-8.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content.
WHST.6-8.9 Draw evidence from informational texts to support analysis, reflection, and research.
Mathematics
6.EE.C.9 Use variables to represent two quantities in a real-world problem that change in relationship to one another; write an equation to express one quantity, thought of as the dependent variable, in terms of the other quantity, thought of as the independent variable. Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables using graphs and tables, and relate these to the equation.
Learning Objectives
Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to:
1. define the term autotroph and producer.
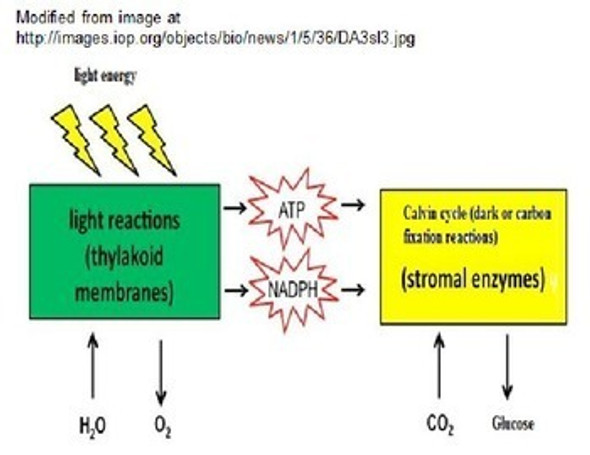
2. state the overall equation for photosynthesis.
3. state the chief purpose of photosynthesis for the producer organism.
4. state several uses for the sugars produced by photosynthesis.
5. state the function of chloroplasts.
6. describe the color and role of chlorophylls in photosynthesis.
7. explain why most why most leaves on plants are usually green in appearance.
8. list the colors used most efficiently and least efficiently by green plants.
9. recognize that chromatography can be used to separate mixtures of plant pigments.
10. explain how the following factors tend to influence the rate of photosynthesis; increased carbon dioxide concentration, increased light intensity, increasing temperature from 0℃ to 30℃ and decreasing available water.
11. briefly explain the cause of Autumn coloration.
12. state the purpose of cell respiration in a living thing.
13. recognize that some form of respiration occurs in all living things all the time.
14. explain how respiration and breathing differ.
15. state the overall equation for aerobic respiration.
16. briefly describe the role of ATP as the energy currency of the cell.
17. identify mitochondria as the sites of aerobic cellular respiration within the cell.
18. compare anaerobic and aerobic respiration in terms of the use of oxygen and ATP output.
19. state the word equation for lactic acid fermentation.
20. recognize that lactic acid build up is associated with muscle fatigue.
21. recognize that lactic acid fermentation is important in the production of some dairy products.
22. state the word equation for alcohol fermentation.
23. explain why alcohol fermentation is important to the brewing and baking industries.
24. explain how photosynthesis is related to cell respiration in terms of energy interactions and gas exchange.
25. recognize light energy from the sun is captured in the bonds of sugar molecules in the process of photosynthesis.
26. explain what is meant by a food chain.
27. write a four step food chain and identify its feeding levels.
28. explain what is represented by the arrow in a food chain or food web.
29. explain the difference between a producer and a consumer organism and identify these in a food chain, food web or energy pyramid.
30. explain what is meant by a primary consumer, secondary consumer and tertiary consumer and identify these in a food chain, food web or energy pyramid.
31. define and list examples of the following terms; herbivore, carnivore, predator, prey, omnivore, scavenger and decomposer.
32. predict how a change in the numbers of a species within a food chain or food web will influence the numbers of other members of the food chain or food web.
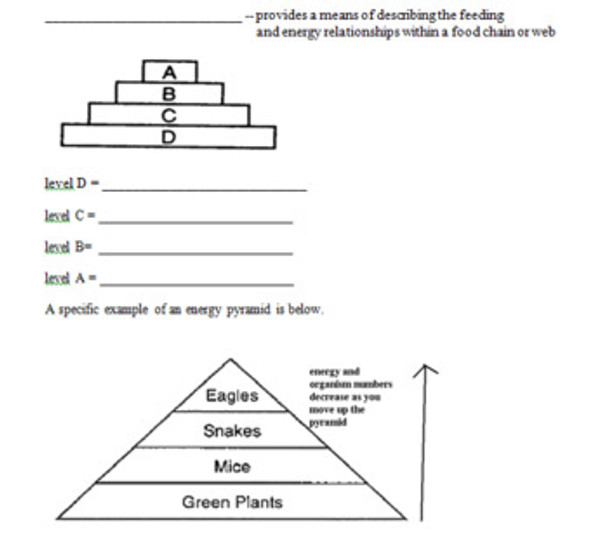
33. explain why the transfer of energy through a food chain, food web or energy pyramid is inefficient.
34. utilize an energy pyramid for describing the feeding and energy relationships within a food chain or food pyramid.
35. label the feeding levels within an energy pyramid.
36. define the terms population, community and ecosystem
37. describe the flow and cycling of matter and energy within an ecosystem.
Terms of Use
Purchase of the product is for classroom use by the purchaser only. It is a violation for individuals, schools, and districts to redistribute or sell this item on the Internet or to other individuals. I do encourage you to use and edit these documents to suit your needs with your own students in distance learning environments.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Visit Monday's Rescue for more great resources!