Description
This zip file contains activities (90 pages of student handouts) which can be used to compose a unit involving Rocks and Minerals. Concepts that are addressed include but not limited to include; minerals, mineral properties, the rock cycle, sedimentary rocks (including clastics, bioclastics, precipitates and evaporites), intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks, metamorphic rocks, contact and regional metamorphism, environments of rock and mineral formation and the economic importance of some rocks and minerals. The learning objectives and specific contents of this set of materials is listed below. This set of activities is suited for many earth science, environmental science or physical science classes. With teacher guidance, many components in these materials are adaptable to an enriched middle level science curriculum.
All documents are in PowerPoint, word or pdf format to allow you to edit the documents to meet your needs. Most of the activities in this package of activities are well suited and easily modified for use in distance learning environments. Answer keys for all student activities are provided.
The specific contents of materials in the package are as follows:
- Learning Goals and Objectives (Including NGSS, Common Core and NY State Earth Science Core Curriculum) (2 pp.)
- Rock and Mineral Completion Notes (18 pp.)
- PowerPoint to accompany the Completion Notes (includes 6 closure/ticket out activities) (77 slides)
- Mineral Identification Lab (8 pp.)
- Minerals and Mineral Properties Worksheet (51 questions) (11 pp.)
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheet 1 (54 questions) (10 pp.)
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheet 2 (45 questions) (13 pp.)
- Rocks and Minerals Worksheet 3 (30 questions) (8 pp.)
- Identifying Minerals Video Worksheet (2 pp.)
- Sedimentary Rocks Video Worksheet (2 pp.)
- Metamorphic Rocks Video Worksheet (2 pp.)
- Igneous Rocks Video Worksheet (2 pp.)
- Rocks and Minerals Exam (50 questions) (12 pp.)
- Rock and Minerals Jeopardy PowerPoint Game (31 questions) (74 slides)
Learning Standards and Objectives
NGSS Standards: Pre-requisite to HSS-ESS-2.A and 3.A
Common Core State Connections:
ELA/Literacy: WHST 9-12.1 Mathematics: MP.2
New York State Physical Setting/Earth Science Core Curriculum
Standard 6 Interconnectedness: Common Themes Models: Key Idea 2
Standard 4: Performance Indicator 2.1: Major Understandings 2.1 w
Standard 4: Performance Indicator 3.1: Major Understandings 3.1 a, 3.1b and 3.1 c
Learning Objectives
Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to:
1. define the terms inorganic and organic.
2. compare and contrast minerals and rocks
3. identify one technology to determine the crystalline structure of a mineral.
4. recognize that oxygen and silicon compose most of the earth's crust by mass.
5. explain what is meant by a silicate.
6. recognize that most rock forming minerals are silicates.
7. describe the structure of the silicon-oxygen tetrahedron that is the basic structure of silicate minerals.
8. explain how inorganic crystallization and recrystallization are involved in the formation of minerals.
9. explain why color is a poor property to use in the identification of most minerals.
10. explain what is meant by streak and how streak plates are used.
11. discuss why streak is a better property to use for mineral identification than color.
12. define the term luster.
13. define the term hardness.
14. explain how Moh's hardness scale can be used to determine the hardness of a mineral.
15. define the terms density and specific gravity.
16. recognize that the density and specific gravity value is specific to each different mineral.
17. explain the difference between cleavage and fracture.
18. describe how the acid test can be used to identify calcite, limestone, dolostone and marble.
19. recognize that halite (rock salt) tastes salty.
20. utilize a reference table to aid in the identification of different minerals.
21. explain what is meant by the texture of a mineral.
22. explain how most sedimentary rocks are formed by compaction and cementation.
23. explain how evaporites are formed and list some examples of evaporites.
24. briefly describe the organic processes involved in the formation of the bioclastic rocks limestone and bituminous coal.
25. list several characteristics of sedimentary rocks.
26. utilize a reference table to assist with the identification of sedimentary rocks.
27. recognize that igneous rocks are formed from molten rock that solidifies.
28. explain how lava and magma are different.
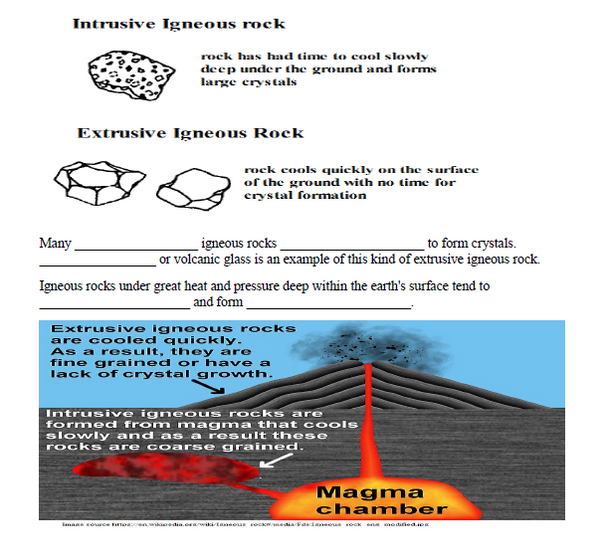
29. contrast intrusive (plutonic) and extrusive igneous rocks in terms of cooling rates, crystal size and environments of formation.
30. explain how vesicular igneous rock form and list an example of a vesicular igneous rock.
31. contrast the composition of felsic and mafic igneous rocks.
32. utilize a reference table to assist with the identification of different igneous rocks.
33. recognize the role of heat and pressure in the formation of metamorphic rocks.
34. explain what is meant by foliation.
35. explain how contact metamorphism occurs.
36. explain why rocks formed through contact metamorphism lack foliation and exhibit transitions from their parent rock.
37. describe how regional metamorphism occurs.
38. recognize that banding is observed in foliated metamorphic rocks.
39. utilize a reference table to assist in the identification of metamorphic rocks.
40. discuss several inferences related to the environments of formation of bituminous coal, limestone, halite, folded metamorphic rocks and extrusive igneous rocks.
41. describe the rock cycle.
42. explain what is meant by a non-renewable resource.
43. state some major economic uses for the following rocks; slate, basalt, coal, pumice, limestone, dolostone, granite and quartzite.
44. briefly describe karst topography and how it is formed.
45. list some major economic uses for the following minerals; quartz, diamond, garnet, graphite, talc and hematite.
Terms of Use
Purchase of the product is for classroom use by the purchaser only. It is a violation for individuals, schools, and districts to redistribute or sell this item on the Internet or to other individuals. I do encourage you to use and edit these documents to suit your needs with your own students in distance learning environments.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.